Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. Syphilis has diverse clinical manifestations and shares many clinical features with other treponemal and nontreponemal diseases (because of this, syphilis has been called “The Great Pretender”). The etiological agent, Treponema pallidum, cannot be cultured, and there is no single optimal alternative test.
Commonly used laboratory diagnostic testing available for syphilis are:
Table of Contents
Direct Diagnosis
Direct laboratory methods for diagnosing syphilis include the detection of Treponema pallidum by microscopic examination of fluid or smears from lesions, histological examination of tissues, or nucleic acid amplification methods such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Tests used for the direct detection of Treponema pallidum are;
Dark-field microscopy
Dark-field microscopy is used to demonstrate the presence of motile Treponema pallidum in lesions or aspirates in early-stage (primary or secondary) syphilis before healing lesions.
Direct fluorescent antibody test for Treponema pallidum
It is a diagnostic method used to detect the presence of T. pallidum in clinical specimens. This test relies on fluorescent-labeled antibodies that specifically bind to T. pallidum antigens. Here’s an overview of how the DFA test for Treponema pallidum is typically performed:
Procedure:
- Specimen Collection: Clinical specimens commonly collected for the DFA test include samples from syphilitic lesions, such as genital sores or mucous patches, as well as cerebrospinal fluid in cases of neurosyphilis.
- Slide Preparation: A thin smear or impression of the specimen is prepared on a glass slide. The specimen is usually fixed to the slide to preserve the integrity of the T. pallidum cells.
- Blocking Solution: The slide is treated with a blocking solution to block non-specific binding of antibodies to the specimen.
- Fluorescent-Labeled Antibodies: Fluorescent-labeled antibodies specific to T. pallidum antigens are applied to the slide. These antibodies are conjugated with a fluorescent dye, allowing for the visualization of the bacteria under a fluorescence microscope.
- Incubation: The slide is incubated to allow the fluorescent antibodies to bind specifically to T. pallidum antigens in the specimen.
- Washing: Unbound or non-specifically bound antibodies are washed away to reduce background fluorescence.
- Microscopic Examination: A fluorescence microscope is used to examine the slide. When exposed to the appropriate wavelength of light, the bound fluorescent antibodies emit light, allowing for the visualization and identification of T. pallidum.
- Interpretation: The presence of characteristic fluorescence in a spirochete-like pattern confirms the presence of T. pallidum in the specimen.
Nucleic acid amplification (PCR based) methods
Nucleic acid-based methods methods are highly sensitive and specific. Here are some standard nucleic acid-based methods used for the detection of Treponema pallidum:
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR):
- Principle: PCR is a widely used nucleic acid amplification technique that amplifies specific DNA sequences. Particular regions of T. pallidum‘s genomic DNA are targeted.
- Procedure:
- A clinical specimen (such as a swab or blood) is collected.
- T. pallidum DNA is extracted from the specimen.
- Primers specific to T. pallidum DNA are used to amplify the target region.
- The amplified DNA is detected using various methods, including gel electrophoresis, real-time PCR, or hybridization-based assays.
- Transcription-Mediated Amplification (TMA):
- Principle: TMA is an isothermal nucleic acid amplification technique that amplifies RNA transcripts. It is often used for the detection of T. pallidum RNA.
- Procedure:
- T. pallidum RNA is reverse-transcribed into complementary DNA (cDNA).
- The cDNA is amplified using TMA.
- Amplified RNA or cDNA is detected using various methods.
- Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP):
- Principle: LAMP is an isothermal amplification technique that amplifies DNA at a constant temperature using a set of specific primers.
- Procedure:
- T. pallidum DNA is amplified using specific LAMP primers.
- The amplification results can be visualized through turbidity, color change, or fluorescence.
- Reverse Transcription-PCR (RT-PCR):
- Principle: RT-PCR is used to detect RNA. It involves reverse transcription of RNA into cDNA followed by PCR amplification of the cDNA.
- Application: RT-PCR can detect T. pallidum RNA, especially in early syphilis cases.
- In Situ Hybridization:
- Principle: In situ hybridization involves using a labeled nucleic acid probe that specifically binds to T. pallidum DNA or RNA in fixed tissue sections.
- Application: This method helps localize T. pallidum in clinical specimens, especially in cases where direct visualization is required.
Indirect diagnosis/serological methods
It is based on serological tests for the detection of antibodies. Serological testing is the mainstay in the laboratory diagnosis and follow-up of syphilis. Serological tests fall into two categories: nontreponemal tests for screening, and treponemal tests for confirmation.
Nontreponemal tests
They measure both immunoglobulin (IgG and IgM) antiphospholipid antibodies formed by the host in response to lipoidal material released by damaged host cells early in infection and lipid from the cell surfaces of the treponeme itself. Commonly used nontreponemal tests are
Rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test
Toluidine red unheated serum test (TRUST)
Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) test
Treponemal Tests
All treponemal tests use Treponema pallidum or its components as the antigen.
Treponemal tests are used as confirmatory tests to verify reactivity in non-treponemal tests. Once positive, treponemal tests remain positive throughout life with or without treatment, so these tests can not be used to know the response to treatment.
Commonly used treponemal tests are:
Fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test (FTA-ABS) test
Treponema pallidum particle agglutination (TP-PA) test
Treponema pallidum Hemagglutination Assay (TPHA)
Flow-chart for laboratory diagnosis of syphilis
If lesion exudate or tissue is available, a direct examination is performed, followed by a nontreponemal serology test. A treponemal test then confirms a reactive nontreponemal test.
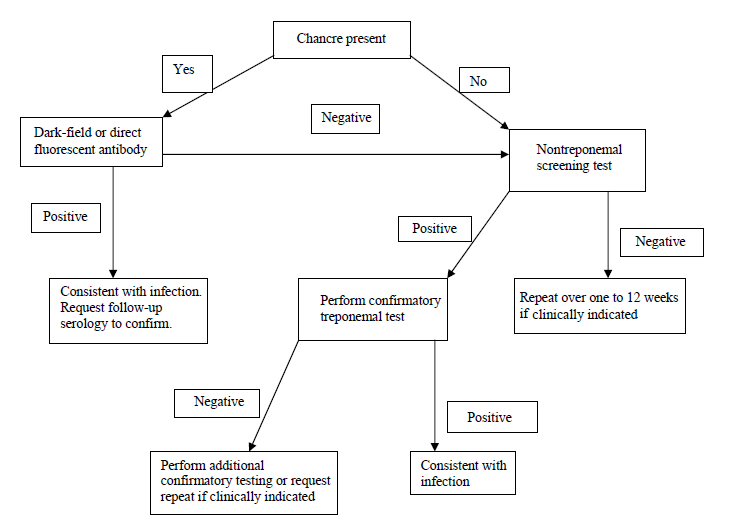
A confirmed serological test result indicates the presence of treponemal antibodies. Still, it does not indicate the stage of disease and, depending on the test, may not differentiate between past and current infections.
References
- Madigan Michael T, Bender, Kelly S, Buckley, Daniel H, Sattley, W. Matthew, & Stahl, David A. (2018). Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition). Pearson.
- Meyer, J. Ch. (1996). Laboratory diagnosis of syphilis. Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1159/000424876
- Larsen, S. A., Steiner, B. M., & Rudolph, A. H. (1995). Laboratory diagnosis and interpretation of tests for syphilis. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 8(1), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.8.1.1


Sir, you are superb.
Plz continue putting posts like these and make our medical life easier.😃
Thanks for your sharing knowledge about microbiology, i wonder if the patient has VDRL neg (-) but TPHA positive(+) 1/80 and clinical symptom is abscent is the patient suffering syphillis or we have to do confirmation test FTA-Abs first before treatment or we can direct give the patient treatment?from Sandi widjaja.