Sulfide Indole Motility (SIM) medium is a differential bacterial growth medium for detecting three different characteristics of an organism;
- Sulfur reduction and (H2S) sulfide production
- Indole production and
- Motility of a bacteria

Sulfur reduction test is useful in differentiating enteric organisms. SIM agar is more sensitive than either TSI or KIA in detecting H2S production. The indole test is one of the IMViC series of tests. The motility test is useful for testing a wide variety of organisms. SIM test is useful for differentiating members of Enterobacteriaceae, primarily for differentiating Salmonella and Shigella.
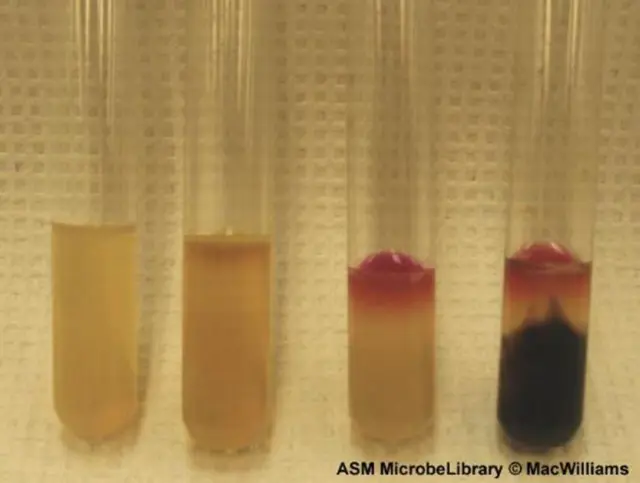
Left: Kligler’s iron agar (KIA) and Right: Sulfide indole motility (SIM) inoculated with weak H2S-producing organism (SalmonellaTyphi). In KIA, blackening is seen in the middle of the tube at the interface of the slant and butt, but in SIM, diffuse delicate blackening is seen across the entire media.
Composition
SIM medium contains a pancreatic digest of casein (casein peptone), a peptic digest of animal tissue (meat peptone), ferrous ammonium sulfate as an iron source, and sodium thiosulfate. Peptone contains amino acids, including tryptophan.
| Ingredients | Amount (gram/liter) |
|---|---|
| Casein peptone | 20 g |
| Meat peptone | 6 g |
| Sodium thiosulfate | 0.3 g |
| Ferric ammonium citrate | 0.2 g |
| Agar | 3.5 g |
| Demineralized water | 1000 mL |
| pH 7.3 ± 0.2 at 25 ° C. |
Principle of Sulfide Indole Motility (SIM) medium
Test organism is inoculated onto semisolid medium sulfide-indole-motility agar and is tested for the production of hydrogen sulfide, indole, and motility of the organism.
Hydrogen sulfide-producing organisms produce H2S gas that reacts with iron salts, ferrous sulfate, and ferric ammonium citrate in SIM, producing a black precipitate.
Indole-producing organisms break down tryptophanpresent in the SIM agar using the tryptophanase enzyme and produce indole. Indole production is detected by Kovac’s or Ehrlich’s reagent, which contains 4 (p)-dimethylamino-benzaldehyde. This reacts with the indole to produce rosindole dye, a red-colored compound.
Nonmotile organisms grow only on the stab line, and the surrounding medium remains clear. Motile organisms move out of the stab line and make the entire tube appear turbid.
Procedure of Sulfide Indole Motility Medium
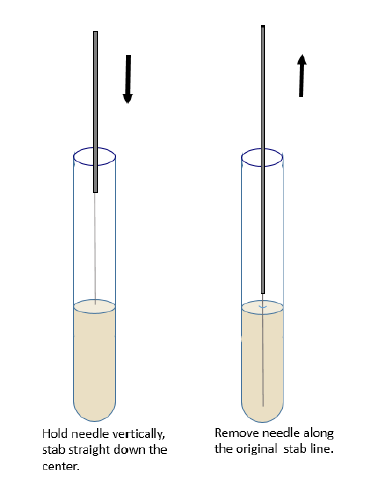
- Label SIM medium with the name of the organisms or lab identification number (whichever is applicable).
- Using a sterile inoculating needle, touch the center of a well-isolated colony. The inoculum should be substantial but does not need to be particularly heavy.
- Aseptically stab once to a depth of 1/3 to 1/4 inch in the middle of the corresponding tube.
- Withdraw the needle and sterilize it by incinerating it in a bunsen burner or micro incinerator.
- Aseptically inoculate the remaining tubes in the same way.
- Incubate aerobically at 35 to 37**°**C for 18 to 24 hours.
Results
Observe for motility and formation of black precipitate before adding a reagent to check for indole production.
| Name of the Organism | Sulfide | Indole | Motility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | No H 2 S | Positive | Motile (Few strains are nonmotile) |
| Vibrio cholerae | No H 2 S | Positive | Motile |
| Citrobacter freundii | Variable | Positive (minority strains give negative results) | Motile |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | No H 2 S | Positive | Motile |
| Enterobacter spp | No H 2 S | Negative | Motile |
| Proteus vulgaris | H 2 S producer | +ve | Motile |
| Proteus mirabilis | H 2 S producer | -ve | Motile |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | No H 2 S | Negative | Nonmotile |
| Yersinia enterocolitica | No H 2 S | Variable | Motile |
| Morganella morganii | No H 2 S | Positive | Motile |
| Providencia spp. | No H 2 S | Variable | Motile |
| Shigella dysenteriae | No H 2 S | Variable | Nonmotile |
| Shigella flexneri | No H 2 S | Variable | Nonmotile |
| Shigella boydii | No H 2 S | Variable | Nonmotile |
| Shigella sonnei | No H 2 S | Negative | Nonmotile |
| Salmonella Paratyphi A | Negative (<13% isolates are H 2 S producers) | Negative | Motile |
| Salmonella Paratyphi B | Positive | Negative | Motile |
| Salmonella Paratyphi C | Positive (minority strains are H 2 S nonproducers) | Negative | Motile |
| Salmonella Typhi | Positive (weak) | Negative | Motile |
| Other Salmonella serovars | Positive (minority strains are H 2 S nonproducers) | Negative | Motile |
Motility
Check for the radiating (fuzzy) growth from the stab line or hold a paper with a print behind the tubes and try to read it through the tubes.
- Motile organisms will spread out into the medium from the site of inoculation.
- Nonmotile organisms remain at the site of inoculation
Find more about motility test medium
Sulfide Production

For sulfur reduction, observe the location of any black color. Blackening usually begins at the inoculation line, and black color may appear throughout the medium or as a black precipitate in the butt.
Indole Test
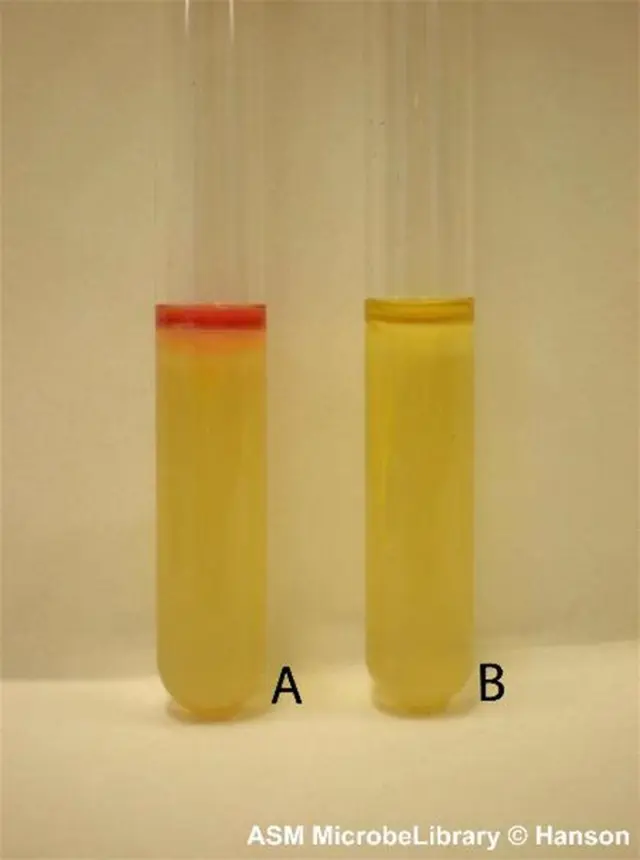
Add a few drops of Kovac’s or Ehrlich’s reagent.
- Positive indole test: Appearance of the red ring after addition of reagent
- Negative indole test: No color change after addition of reagent
Read more about Indole Test
SIM test results of selected bacteria
*Shigella sonnei is indole negative, and other shigellae give variable indole reactions. Salmonellaserovars are indole negative. Klebsiella oxytoca is indole positive.
Similar Types of Biochemical Media
- Motility-indole-ornithine agar
- Motility indole urease medium
References and further readings
- Alternative Methods for Determining Indole Production using SIM medium images. ASM Education
- Sulfur, Indole, Motility (SIM) Media. University of Wyoming. Retrieved 8 October 2022, from http://www.uwyo.edu/molb2021/additional_info/summ_biochem/sim.html
- SIM Medium. Microbugz. Retrieved 8 October 2022, from https://www.austincc.edu/microbugz/sim_medium.php