DNA hydrolysis test or Deoxyribonuclease (DNase) test is used to determine the ability of an organism to hydrolyze DNA and utilize it as a source of carbon and energy for growth.
DNase agar is a differential medium used to test an organism’s ability to produce deoxyribonuclease or DNase. This medium is pale green in color because of the DNA-methyl green (indicator) complex (Note: Methyl green is a cation that binds to the negatively-charged DNA). It also contains nutrients for the bacteria.
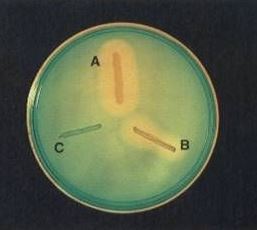
If the organism that grows in the medium produces Deoxyribonuclease, it breaks down DNA into smaller fragments. When the DNA is broken down, it no longer binds to the methyl green, and green color fades and the colony is surrounded by a colorless zone(See fig-1).
Requirements
- **Media:**DNase Agar or DNase agar with Methyl green indicator.
- Reagent: Hydrochloric acid (1mol/L) only when DNase agar without an indicator is used
- Others: Inoculating loop, Bunsen burner
Procedure of DNase (DNA hydrolysis test)
- Dry the surface of agar plates before use**.**Each plate may be divided into sections by drawing lines on the bottom of the plate.
- Inoculate the test agar medium: There are two types of inoculation that can be done.
Spot Inoculation
- Touch a colony of the organism under test with a loop and inoculate it onto a small area of the DNase test agar plate, in the middle of one of the marked sections to form a thick plaque of growth 5-10 mm in diameter after incubation.
- Incubate the plate at 37°C for 18-24hr.
Band or line streak inoculation
- Use a heavy inoculum and draw a line 3-4 cm long from the rim to the center of the DNase test agar plate
- Incubate the plate at 37°C for 18-24hr.
- When using DNase agar without the indicator,
Flood the plate with 1N Hydrochloric Acid. Leave the plate to stand for a few minutes to allow the reagent to absorb into the plate. Decant excess hydrochloric acid and then examine the plate within 5 minutes against a dark background.
Expected results
- Positive: When DNA is hydrolyzed, methyl green is released turning the medium colorless around the test organism.
- Negative: If there is no degradation of DNA, the medium remains green.
Test results
- DNase Test positive organisms:
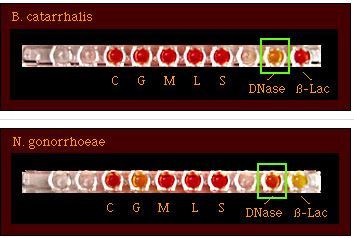
Serratia marcescens Staphylococcus aureus Campylobacter jejuni (some strains) M. Catarrhalis
- DNase test negative organisms:
Staphylococcus epidermidis Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Uses of DNase Test
- It is used to differentiate S.aureus (DNase +ve) from other Staphylococci that do not produce such enzyme. The DNase test is particularly useful when plasma is not available to perform a coagulase testor when the results of a coagulase test are difficult to interpret.
- DNase test distinguishes M. catarrhalis from all other gram-negative diplococci (e.g. Neisseria gonorrhoeae & Neisseria meningitidis) of human origin.
Limitation of DNase Test
- Some MRSA strains do not give positive DNase test result and some strains of the coagulase-negative staphylococci such as Staphylococcus capitis may give weak reactions.
- Serratia and Moraxella species also produce deoxyribonuclease.
- 1N HCl is bactericidal for Staphylococci. Once the HCl has been applied, the test must be read within 5 minutes and cannot be continued by re-incubation.
References
- Winn, W. C., & Koneman, E. W. (2006). Koneman’s Color Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology (Color Atlas & Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
- Pimenta, F. P., Souza, M. C., Pereira, G. A., Hirata, R., Jr, Camello, T. C., & Mattos-Guaraldi, A. L. (2008). DNase test as a novel approach for the routine screening of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Letters in applied microbiology, 46(3), 307–311. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2007.02310.x
- Kateete, D. P., Kimani, C. N., Katabazi, F. A., Okeng, A., Okee, M. S., Nanteza, A., Joloba, M. L., & Najjuka, F. C. (2010). Identification of Staphylococcus aureus: DNase and Mannitol salt agar improve the efficiency of the tube coagulase test. Annals of clinical microbiology and antimicrobials, 9, 23. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-0711-9-23