All living cells can be classified as either prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Bacteria are prokaryotic or prenuclear organisms (organisms without a true nucleus), while fungi, protozoa, helminths, and other organisms are eukaryotic.
Viruses depend on host cells for survival, so they are not considered cellular organisms but infectious agents. Prions (abnormal infectious proteins) are also not considered living cells.
A notable characteristic of eukaryotic cells is the presence of membrane-enclosed subcellular organelles with specialized cellular functions such as mitochondria (sites of aerobic respiration) and chloroplasts (sites of photosynthesis in green plants).
- Endoplasmic reticulum processes and transport proteins.
- Lysosomes provide an environment for controlled enzymatic degradation of intracellular substances.
- Mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell; it generates energy (ATP)
- The nucleusprovides a membrane enclosure for chromosomes.
- The Golgi bodytransports substances throughout the cell, including internal delivery and exocytosis or secretion of molecules.
Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, do not contain organelles. All functions take place in the cytoplasm or cytoplasmic membrane of the cell. The cell wall composed of peptidoglycan is the notable structure present only in prokaryotic bacterial cells.
Eukaryotic cells have a cytoskeleton that supports cellular structure, organization, and movement. The cytoskeleton plays an essential role in immunology by mediating phagocytosis.
Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells differ considerably at the macromolecular level, including chromosomal organization, gene expression, and protein synthesis machinery. For example;
- Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus with a nuclear membrane enclosing multiple chromosomes, while prokaryotic cells have a single chromosome (nucleoid) that is not enclosed in a nuclear membrane.
- Another major difference between bacterial DNA and eukaryotic DNA is that bacterial DNA has no introns, whereas eukaryotic DNA does.
- A key genetic difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is that eukaryotes typically contain two copies of each gene and are, thus, genetically diploid.
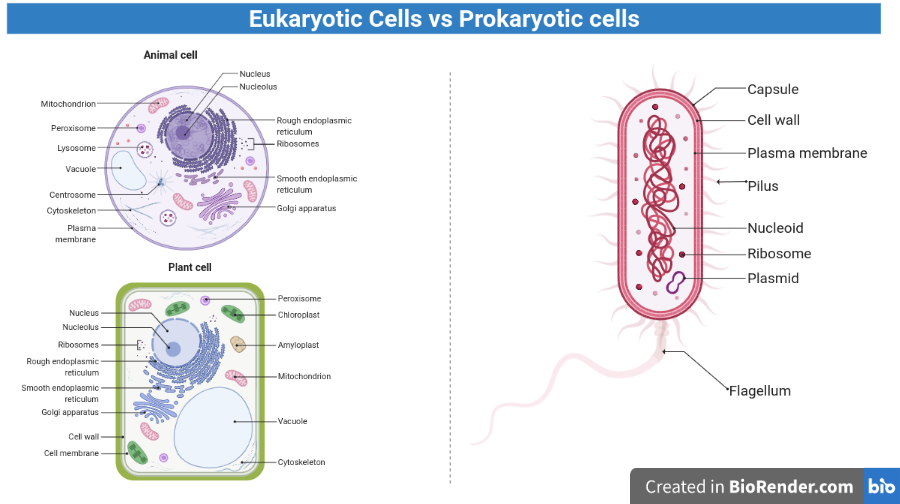
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ substantially in many other characteristics, some of which are tabulated here:
References
- Madigan Michael T, Bender, Kelly S, Buckley, Daniel H, Sattley, W. Matthew, & Stahl, David A. (2018). Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition). Pearson.
- Pelczar Jr., M., Chan, E., & Krieg, N. (2007). Microbiology (5th edition). Tata McGraw-Hill