Lactobacillus MRS Broth test is used to test gas production by Gram-positive rods in a glucose-containing medium**.**MRS is an acronym for the authors of this publication (De Mann JD, Rogosa, and Sharpe), who suggested this medium for the cultivation of lactobacilli.
MRS broth test determines whether gram-positive bacilli form gas during glucose fermentation. MRS broth test is helpful to differentiateLeuconostocspp., which produces gas from Lactobacillusspp, which is gas negative. Weissella confusais also a gas producer, whereas streptococci and Pediococcus do not produce gas.
Principle
MRS broth is a selective medium that uses sodium acetate and ammonium citrate to prevent overgrowth by contaminating organisms. It contains sources of carbon, nitrogen, and vitamins to support the growth of lactobacilli and other gram-positive organisms.
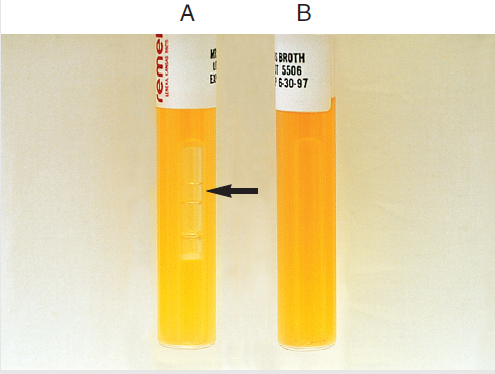
Growth is considered a positive result. A Durham tube can be added to the MRS broth to detect gas production. A rise in a petroleum jelly plug or displacement of broth with air in the Durham tube suggests gas production. Ordinary sugar fermentation tubes cannot detect these organisms because of a lack of sufficient gas production.
Materials
- Sterile sticks
- Incubator
- Gas detection optionsVaspar, liquid paraffin, or petroleum jelly, maintained at 56°C in liquid form.Durham tube
- Test organism: Gram-positive coccobacilli that are catalase-negative, PYR-negative, vancomycin-resistant, and grow aerobically.
- MRS Broth
| Ingredients | Amount (Gram/liter) |
|---|---|
| Enzymatic digest of animal tissue | 10 g |
| Beef extract | 10 g |
| Yeast extract | 5 g |
| Dextrose | 20 g |
| Polysorbate 80 | 1 g |
| Ammonium citrate | 2 g |
| Sodium acetate (NaC 2 H 3 O 2 ) | 5 g |
| Magnesium sulfate (MgSO 4 ) | 0.1 g |
| Manganese sulfate (MnSO 4 ) | 0.05 g |
| Dipotassium phosphate | 2 g |
| Agar | 15 g |
| Final pH: 6.5 |
Quality Control
Perform quality control (QC) on each new lot or media shipment, using positive and negative control before using them. Inspect the broth for lack of turbidity. Invert if there is a Durham tube and it contains a bubble.
- Positive (growth with no-gas production): Lactobacillus lactis (ATCC19435)
- Positive (growth with gas production): Leuconostoc mesenteroides ATCC 10830
- Negative (no growth, no gas production): Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212
Method
Results
- Positive: Leuconostocspp. growth; gas production indicated by the trapped gas bubble in the Durham tube. Suppose vaspar plug is used instead of Durham tube, visible lifting of the plug and its complete separation from the broth surface is seen.
- Positive: Lactobacillusspp.—growth; no gas bubble in the Durham tube or no lifting of the wax plug.
- Negative: No growth (not shown).
Limitations
Since strains of Leuconostoc produce copious amounts of gas, the Durham tube is a safer alternative to petroleum jelly. However, the Durham tube method does not work as well.
References and further readings
- Bailey & Scott’s Diagnostic Microbiology, Forbes, 11th edition
- Andrea J. Linscott, 2016. *Clinical Microbiology Procedures Handbook,*4th Edition. ASM Press, Washington, DC. doi: 10.1128/9781683670438.