In this blog post, I am posting 10 Multiple Choice Questions (21-30) which cover various topics/areas of virology. If you have not attempted MCQs (1-10 and 11-20), I recommend you to give the shot. Answer keys and explanations of some of these questions are available at the end of this blog post.
I request you to take a copy and a pen or pencil and jot down your answer before checking the answer and/or descriptions.
-
What is the most common cause of aseptic meningitis of viral etiology?a. Enterovirusesb. Herpesvirusesc. Arbovirusesd. Retrovirusese. Orthomyxoviruses
-
Protection against influenza A virus in a nonimmune individual can be achieved through the administration of a drug that interferes witha. viral endonuclease activityb. binding of host messenger RNA (mRNA) caps by the viral P1 proteinc. synthesis of viral progeny RNAd. uncoating of nucleic acide. viral adsorption and penetration
-
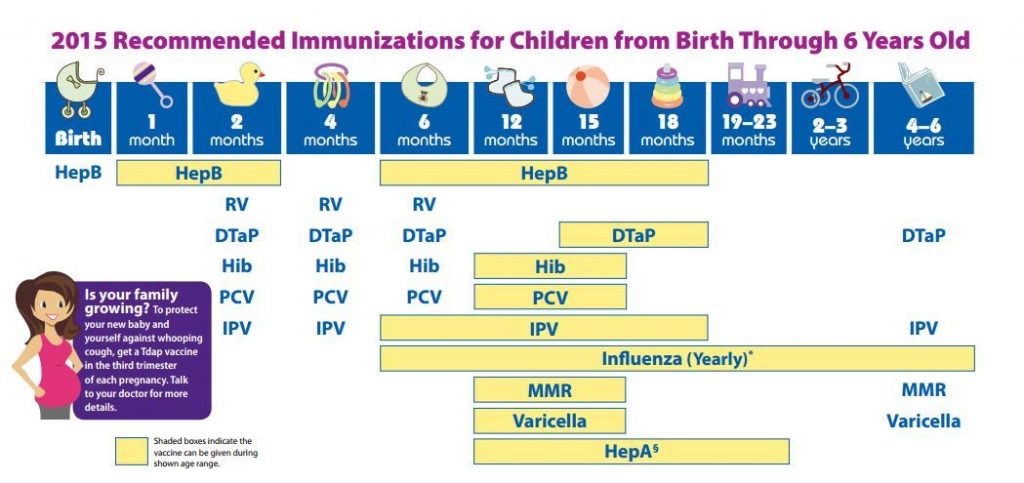
Which one of the following immunizations should be administeredimmediately after birth?a. Diphtheria-pertusis-tetanus (DPT) vaccineb. Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccinec. Hepatitis B vaccined. HIV Vaccinee. Oral Poliovirus
-
Which one of the following infection routes aremost often involved in the neonatal transmission of hepatitis B virus (HBV)?a. Blood transfusionb. Fetal contact with infected blood during childbirthc. Ingestion of the virus via maternal breast milkd. Transmission of the virus from hospital personnel during childbirthe. Transplacental transmission of the virus
-
The finding of large, multinucleated, clumps of cells in the bronchial secretions of a 2-year-old girl with acute bronchopneumonia suggests that this infection is caused bya. Bordetella pertusisb. Epstein-Barr virusc. Mycoplasma hominisd. Rhinoviruse. Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
-
All of the following picornaviruses are resistant to the acidity of the stomach except:a. Coxsackievirus Ab. Coxsackievirus Bc. Echovirusd. Polioviruse. Rhinovirus
-
A divorced mother of four tests positive for HIV-1 Infection during an investigation of a febrile illness with disseminated lymphadenopathy. A second enzyme immunoassay (EIA) is performed, and the results are the same. The woman denies intravenous drug use. She has dated several men since her divorce and can not be positive about their sexual habits or use of intravenous drugs. What is the appropriate next step in the management of this patient?a. Treatment with zidovudine (azidothymidine, AZT)b. All the patients’ close contacts should be tested for HIV antibodiesc. The public health authorities should be notifiedd. A western blot (immunoblot) test should be orderede. The patient should be reassured and told that her disease is probably unrelated to AIDS.
-
In a chronic carrier of hepatitis B virus (HBV), which positive test is most indicative of high infectivity?
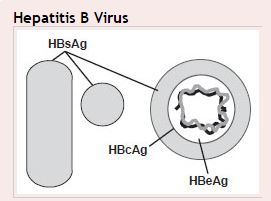
a. Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HbsAg)b. Hepatitis B Core Antigen (HbcAg)c. Hepatitis B e Antigen (HbeAg)d. Anti-HBsAge. Anti-HBeAg
-
A retrovirus is found in a high proportion in laboratory animals of a given species. Most viremic animals are asymptomatic, but others develop a fatal wasting syndrome, and a few develop leukemia and other tumors after long periods of latency. The virus in question most likely lacks which one of the following genes?a. gagb. polc. envd. onc
-
A sexually active 22-year-old college student presents to the local clinic with a localized vesicular eruption on the shaft of his penis. A scraping of the base of one of the vesicles is positive for Tzanck cells. The patient mentions that he had a similar eruption in the same area 2 months earlier. The reappearance of this eruption may be explained by:a. Cell-mediated immunity (CMI) deficiency in the patientb. A prolonged period of viremia following the initial infectionc. A second infection with a similar virus with a different serotyped. failure of the patient to comply with therapy prescribed at the initial episodee. reactivation of a latent infection.
Answers Key (MCQ Virology (21-30)
-
a.Enteroviruses
-
Try yourself
-
c. Hepatitis B Vaccine****Explanation: First dose of both DPT (or DTaP), Haemophilus influenzae b (Hib), and inactivated poliovirus (IPV) vaccine are given at 2 months of age. Currently, there is no vaccine to prevent HIV. WHO recommends that all infants should receive their first dose of Hepatitis B vaccine soon after birth, preferably within 24 hours of birth.
-
Try yourself
-
e. Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). These large multinucleated epithelial cells are also known as syncytia; from which the virus derives its name.
-
e. Rhinoviruses****Explanation: Polio, Coxsackie A and B, and Echo viruses fall under the genera Enterovirus and are resistant to acid pH. Rhinoviruses are labile to acid pH.
-
Try yourself
-
**c. Hepatitis B e Antigen (HbeAg)**Explanation: (HBeAg is detected in the serum of persons with high virus titers and indicates high infectivity). Read more about the interpretation of serologic results for Hepatitis B testing HERE
-
Try yourself
-
Try yourself