T cells and B cells are white blood cells that are important cells for adaptive immunity. Like all blood cells, they are made in the bone marrow. While B-cells mature in the bone marrow, T-cells travel through the bloodstream to the thymus (a small organ between the lungs and behind the sternum) and mature there. Broadlyspeaking T cells can be divided into two different types, ‘killer T-cells’ and ‘helper T-cells’.
Regulatory T cells (also called Tregs) areanothertypes of T cells.Tregs have a role in regulating or suppressing other cells in the immune system. 2018 Nobel prize in Physiology and Medicine is related to negative immune regulation. Find more innobelprize.org
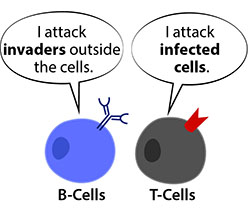
Killer T cells also known as cytotoxic T cells (CTL) hunt down and destroy cells that are infected with germs or that have become cancerous while helper T cells help B cells to make antibodies. T helper (TH) cells express CD4 molecules and are restricted to recognizing antigens bound to class II MHC molecules, whereas T cytotoxic (TC) cells express CD8 and are restricted to recognizing antigens bound to class IMHC molecules. Cytotoxic T cells kill cells that are infected with viruses or altered self-cell with toxic mediators (perforin and granzymes).
B cells are major cells of humoral (antibody-mediated) immunity, effector B cells (plasma cells) produce antibodies that circulate, capture and destroy antigens.
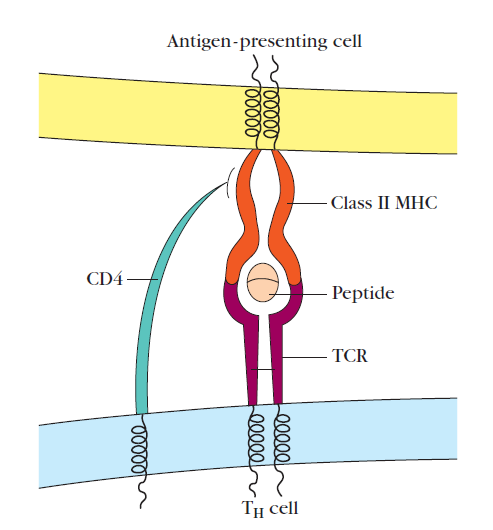
Circulating helper T cells recognize exogenous antigens and produce cytokines. Two major groups of helper T cells are known as Th1 and Th2 cells. Th1 cells predominantly produce interferon-g (IFN-g), which promotes cell-mediated immune mechanisms. Th2 cells produce mostly interleukin-4 (IL-4), which promotes humoral immunity by activating B cells.
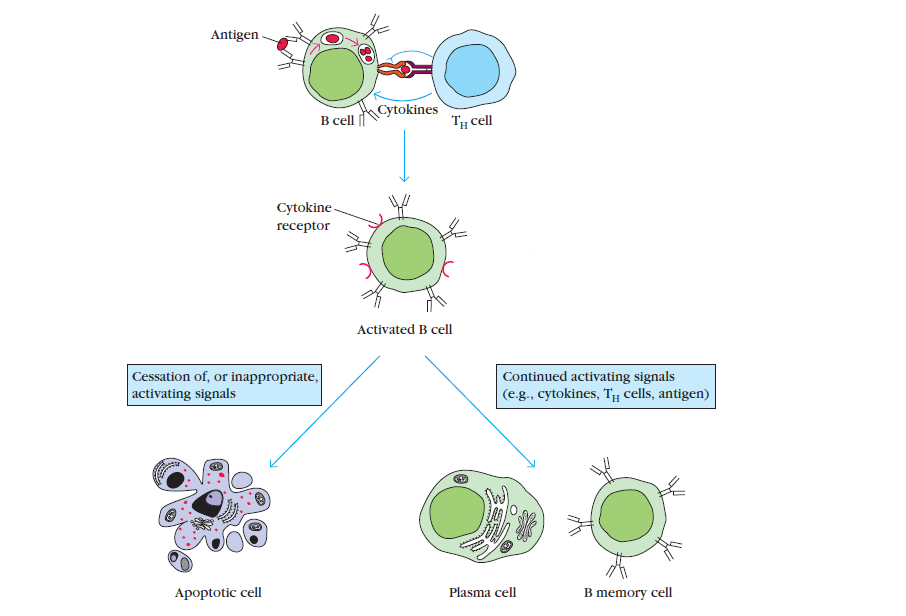
When a naïve (virgin) B cell first encounters the antigen that matches its membrane-bound antibody, the binding of the antigen to the antibody causes the cell to divide rapidly (clonal expansion); its progeny differentiates into memory B cells and effector B cells called plasma cells. Plasma cells secrete antibodies which act as major effector molecules of humoral immunity.
Some of the major differences between B Cells and T Cells are tabulated below:
References and further reading:
- Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 9th Edition
- Kuby Immunology, 8th Edition
- Roitt’s Essential Immunology, 13th Edition